Embodied Carbon

Despite being a significant source of carbon emissions in the UK, embodied carbon emissions are currently unregulated, and measurement and mitigation within construction is typically voluntary. As highlighted by UKGBC’s Net Zero Whole Life Carbon Roadmap, the accurate and consistent measurement and reporting of embodied carbon has become increasingly important to ensure meaningful and credible progress towards net zero carbon goals.
To achieve this, it’s essential that embodied carbon moves quickly from being a challenge only addressed by leading organisations, to one that is tackled by stakeholders across the built environment industry.
What is Embodied Carbon?
Embodied carbon refers to the emissions associated with materials and construction processes throughout the whole lifecycle of a building or infrastructure. This is typically associated with any processes, materials or products used to construct, maintain, repair, refurbish and repurpose a building.
Check out UKGBC’s explainer guide for more information on embodied carbon. These guides are written to demystify key sustainability concepts and create a common language for non-technical experts to confidently get involved in sustainable building topics.

What do we need to reduce embodied carbon in the built environment?
We need greater consistency from industry when modelling embodied carbon
We need greater transparency within the modelling and reporting process
We need responsible regulation from Government to accelerate industry action on embodied carbon
We need an official education route to improve the expertise of assessors
Projects and Resources
Latest Report
Embodied Carbon Scope 3 Measurement and Reporting
This new report seeks to align organisational GHG Scope 3 reporting and project-based embodied carbon assessments to show how establishing a coherent link can support emissions reductions efforts. The guidance demonstrates that integrating embodied carbon assessments directly within Scope 3 reporting would represent an easier, more centralised and more detailed solution than typical practices for GHG Protocol reporting.

Improving your modelling and reporting
Guidance for industry professionals
This report focuses on refining and improving the practices of embodied carbon modelling and reporting within the construction industry. It is aimed at practitioners undertaking embodied carbon modelling, and especially those who are new to the practice.
Widespread embodied carbon reporting is essential for the construction industry to effectively address its environmental impact and, as the practice is undertaken with increasing frequency, it’s important to ensure that it continues to be rigorous and reliable. Moving to greater transparency and consistency will enable informed decision-making and more sustainable practices across the construction sector.

Practical Guidance
How to write a project brief for embodied carbon assessments
This guide is designed for those who need to write effective briefs for commissioning their first embodied carbon measurements, but who may be at an early stage of embodied carbon knowledge. It is not a how-to guide for measuring carbon, or which method or tools should be adopted. The guidance provides straightforward information on how to develop a brief and ‘get the job done’.
Embodied Carbon as part of the bigger picture
Whole Life Carbon Roadmap
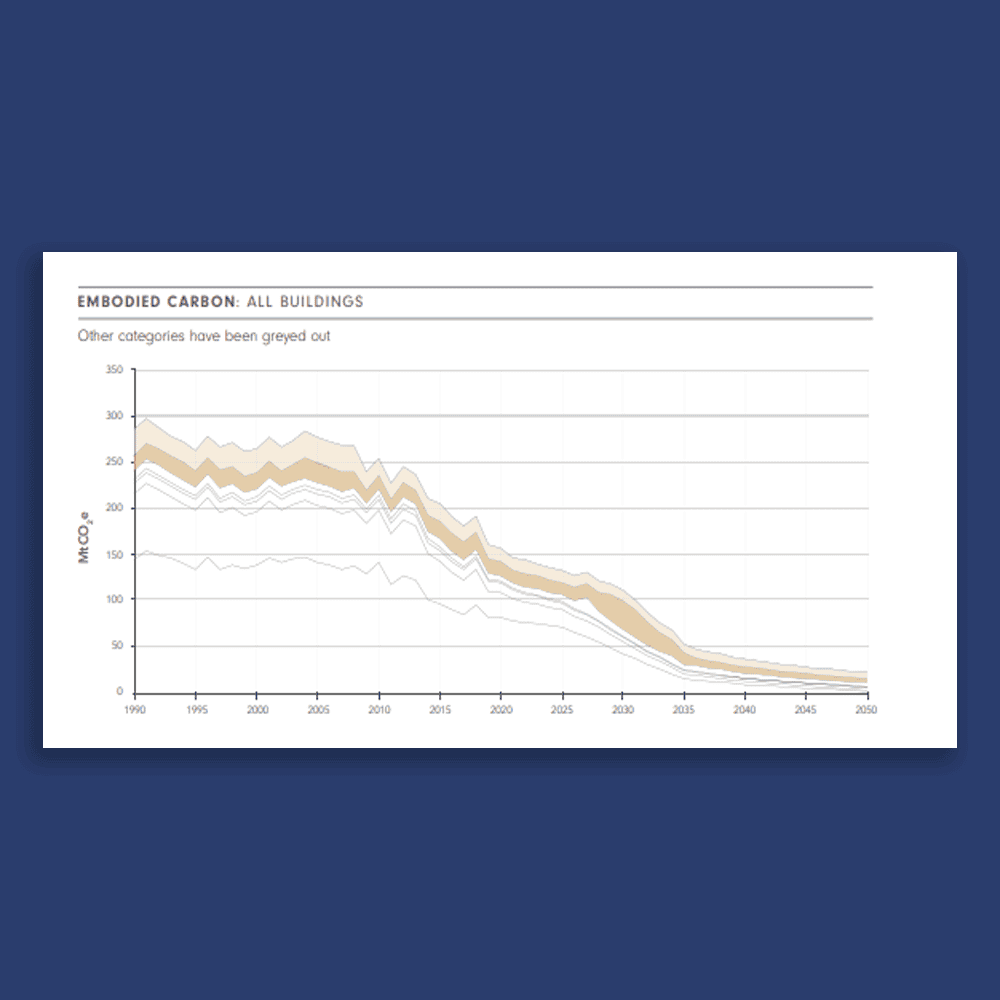
The Roadmap was launched at the beginning of a crucial decade for climate action, with the need for our industry to decarbonise clearer than ever. Critically, the trajectory demonstrates to industry and government that there is a clear pathway to net zero by 2050 for the built environment, setting out step-by-step actions for different stakeholders.
Embodied carbon from the construction and refurbishment of buildings makes up 20% of built environment emissions. Embodied carbon emissions are currently unregulated, and measurement and mitigation within construction is typically voluntary.
Legislation to measure and limit embodied carbon must be introduced at the earliest opportunity, alongside support for industrial decarbonisation of key material supply chains and reduced demand for new construction and materials through increased design efficiency, re-use and circularity.
Related Resources
Embodied Carbon Modelling and Reporting

Embodied Carbon – Practical Guidance

Guide to Scope 3 Reporting in Commercial Real Estate

How Circular Economy Principles can impact carbon and value

Events
Embodied Carbon and Scope 3 Reporting Guidance Launch

Writing Whole Life Carbon Assessment reports in the Built Environment – A Masterclass (London)

Advancing Net Zero Showcase – London

Embodied Carbon Modelling and Reporting Guidance Launch

News & Blogs
UKGBC tools up to tackle embodied carbon at critical moment for delivering net zero

Circular development and net zero construction: a commercial office in the heart of Edinburgh

Beyond the building: reducing embodied carbon through innovative master planning

Challenges and Opportunities with Scope 3 in Commercial Real Estate

Advancing Net Zero Partners
Our Advancing Net Zero work is made possible thanks to our programme partners











Embodied Carbon Project Partners
Our Embodied Carbon measurement and reporting project is made possible due to the generous support of our project partners.






