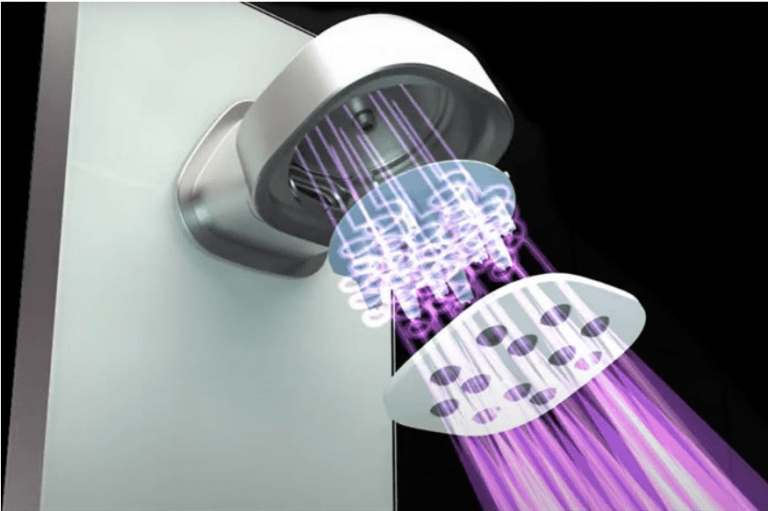
Shower Sensor to Reduce Water Usage
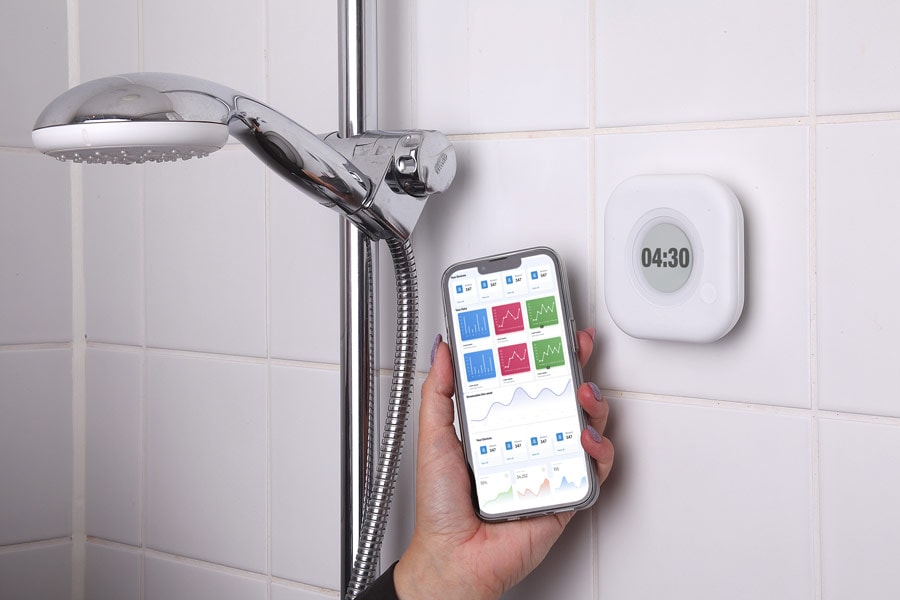

Problem Addressed
Statistics collected by the Energy Saving Trust show that showers and baths are responsible for the highest percentage of water usage in an average household. With an average shower length between 6-8 minutes and an average flow rate of 12 litres per minute, reducing shower length by 2-3 minutes daily could save between 5,200 to 9,360 litres of water per person per year. By reducing hot water consumption, this would also reduce energy use and CO2 emissions.
Case Study
Aguardio Shower Sensors were tested in seven tourism accommodations in Europe and North America. Over 25,488 showers were measured to test the effectiveness of real-time feedback on shower duration. Guests were given persuasive messages reflecting pro-environmental values to encourage shorter showers. The result was that the average duration of showers was reduced by 13.56% on average, with the most effective messaging tested resulting in a 21.27% reduction across all the accommodations. Per room per year, this intervention would save 4.44 M3 of water, 0.19 MWH of energy, and 33kg of CO2.
Facts and Figures
This page presents data, evidence, and solutions that are provided by our partners and members and should therefore not be attributed to UKGBC. While we showcase these solutions for inspiration, to build consensus, and create momentum for climate action, UKGBC does not offer commercial endorsement of individual solutions. If you would like to quote something from this page, or more information, please contact our Communications team at media@ukgbc.org.
Related
Toilet Leak Sensors

Platform for leak detections and water analytics
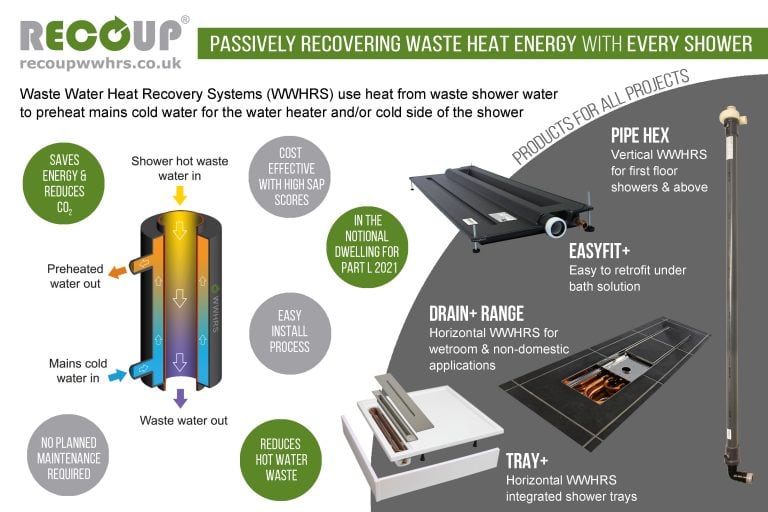
Waste water heat recovery system for showers
Water and energy efficient showers

