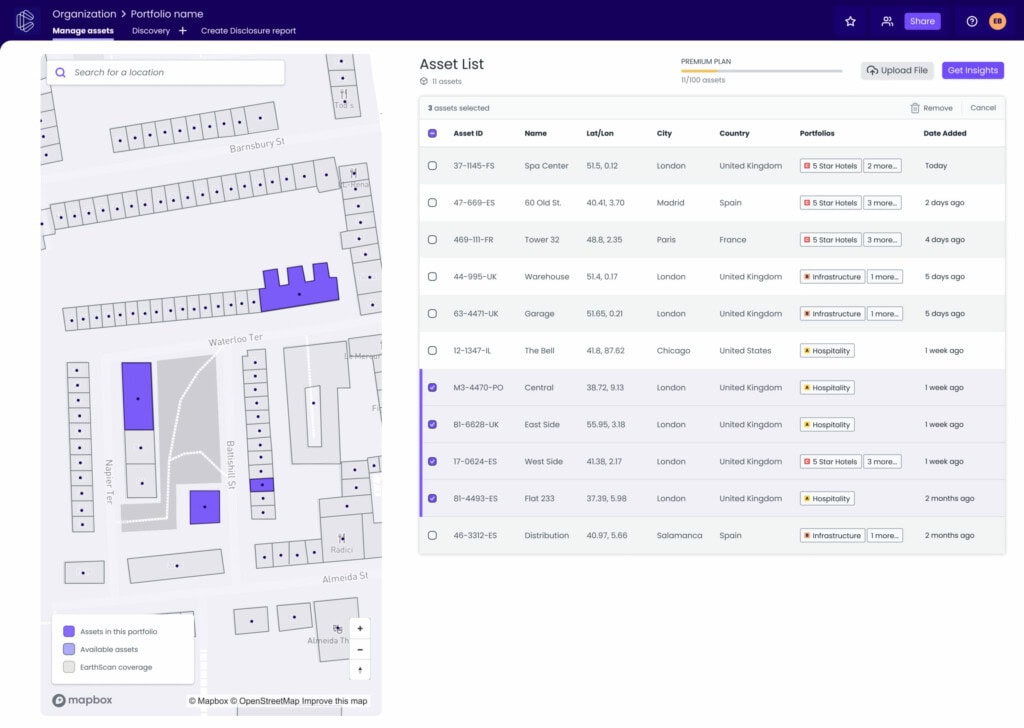
Climate risk platform
Problem Addressed
This solution was sourced in response to UKGBC’s Innovation Challenge: “How can existing buildings be made more resilient to climate change, with as little disruption to their occupants as possible, by 2030?”
Climate uncertainty makes adaptation and resilience decisions radically more difficult for organisations. 90% of decision makers in a Cervest survey said extreme weather affected at least one of their company’s physical assets in the past 5 years. Yet, only half said climate change is factored into risk planning.
Verification & Case Study
Effectiveness can be assessed through:
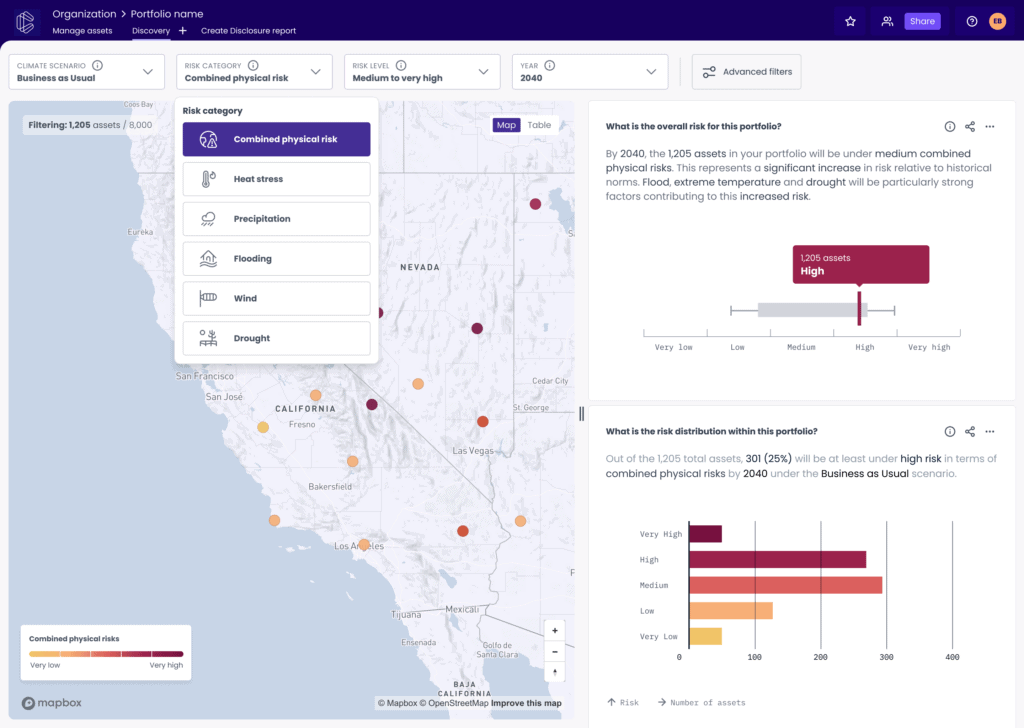
- The cost-savings associated with preventing asset damage and losses. Key outcome: relationship with climate risk shifts from reactive to proactive — taking early interventions on our most critical assets.
- Adoption by multiple parties using EarthScan to implement risk mitigation strategies / make adaptation decisions based on the single source of truth. Key outcome: A shared view of risks allows multiple parties to baseline, benchmark, segment, and rectify risks on ‘assets of common interest’ – unlocking new conversations and ‘change’ incentives for the first time.
- The network effect of multiple parties using the same Climate Intelligence source to make decisions drives behaviour change at scale. Key outcome: a Climate Intelligence Network that unlocks radical transparency at asset-scale, enabled by harmonised ratings, sharing, and integration into key decisions and investments by banks, insurers, supply chains, customers and governments.
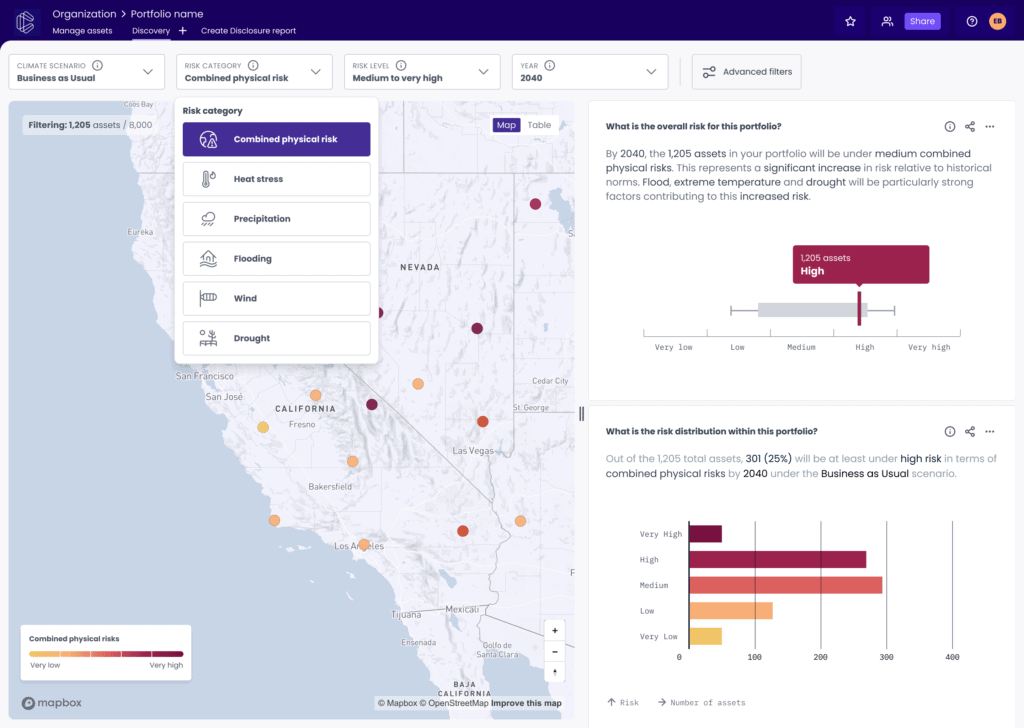
Use Case #1:
A large healthcare institution is using EarthScan to assess the climate risks threatening their assets. Assets must continue to function while refurbishments are underway. They used EarthScan to analyse heat stress across their primary sites. EarthScan showed that over a short-term time horizon, many assets would face increased levels of max temperature and heat wave days, posing a threat to occupants and operational uptime. Using this intelligence, the organisation reviewed and amended their HVAC systems across assets most at risk, adapting each one with necessary systems to mitigate against this scenario.
Use Case #2:
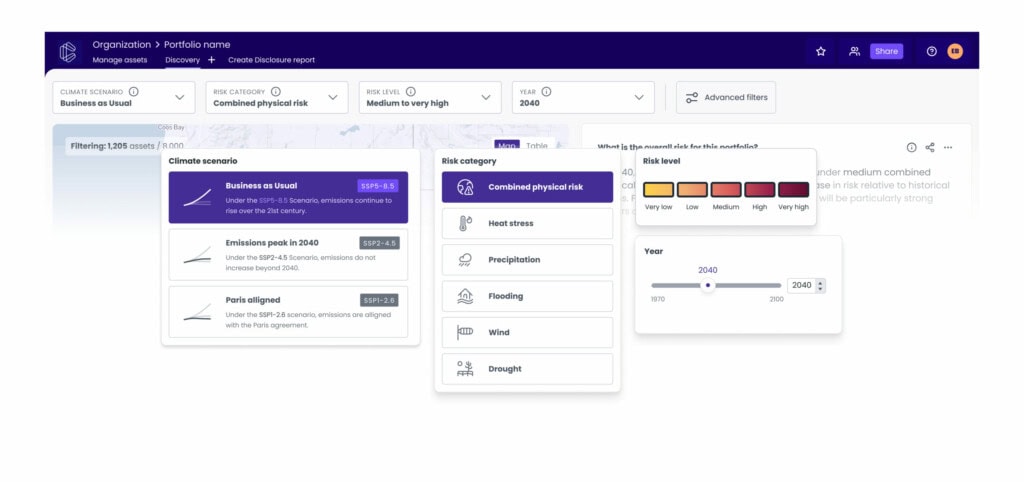
An architecture firm is using EarthScan to inform pre-development design and construction decisions. It’s conducting greenfield and brownfield climate risk assessments on commercial real estate developments. The firm uses EarthScan’s insights across different climate hazards to inform the building materials needed to withstand specific risks. For example, EarthScan revealed a large reduction in wind speed on one development, meaning the building would endure a reduction in natural air flow. In response, the customer designed appropriate HVAC systems. By examining the symbiotic nature of climate change and anthropogenic air pollution, the architects included more windows (to increase natural air flow) that were double-glazed (less pollution coming in).
Facts and Figures
This page presents data, evidence, and solutions that are provided by our partners and members and should therefore not be attributed to UKGBC. While we showcase these solutions for inspiration, to build consensus, and create momentum for climate action, UKGBC does not offer commercial endorsement of individual solutions. If you would like to quote something from this page, or more information, please contact our Communications team at media@ukgbc.org.
Related
Green roofs for people and nature

Database of sustainable building products
Paradise 11

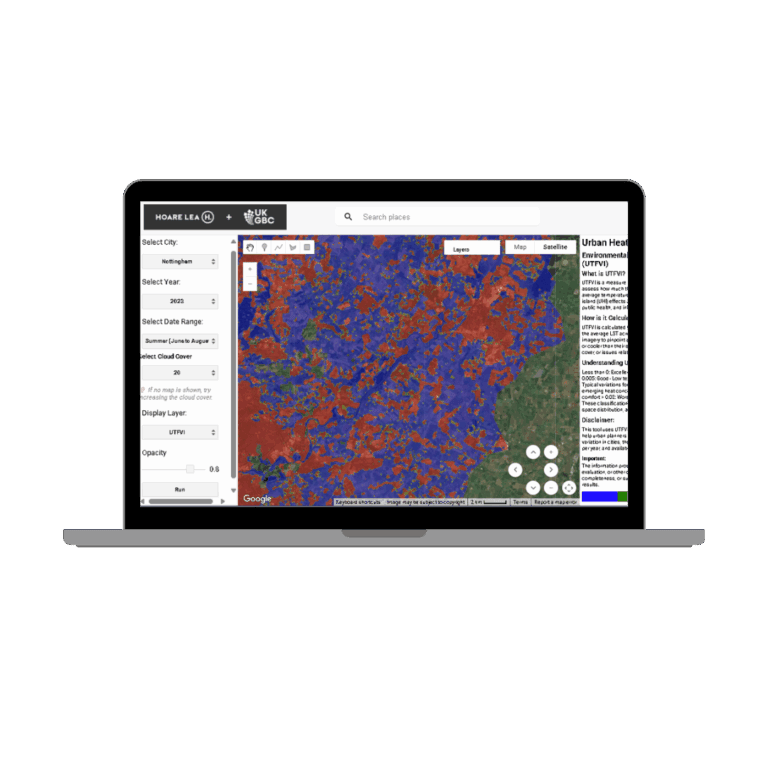
Urban Heat Island Web Map